Emerging Role of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Recent Results in Cancer Research 191

4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2943 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 320 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Inflammation has long been recognized as a key player in various chronic diseases, including cancer. In recent years, the scientific community has witnessed an explosion of research investigating the potential of anti-inflammatory drugs as a promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment. This article delves into the latest advancements in this field, exploring the mechanisms, efficacy, and potential of anti-inflammatory drugs in reshaping the fight against cancer.
Understanding Inflammation and Cancer
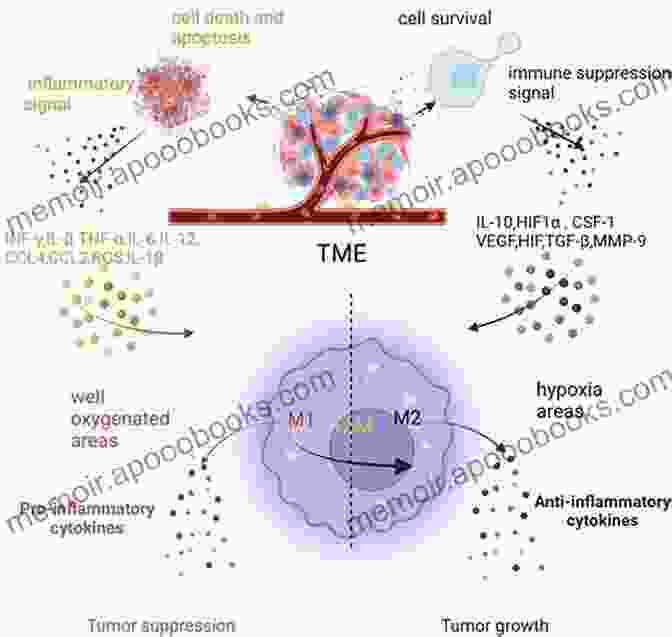
Inflammation is a complex biological response to injury or infection, characterized by the recruitment of immune cells to the site of damage. While inflammation is essential for healing and tissue repair, chronic inflammation can contribute to the development and progression of various diseases, including cancer.
In cancer, inflammation can promote tumor growth, angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels),invasion, and metastasis. Inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and chemokines, can stimulate cancer cell proliferation, survival, and migration, creating an environment conducive to tumor development and spread.
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: A Novel Therapeutic Approach
Given the role of inflammation in cancer, targeting inflammatory pathways has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy. Anti-inflammatory drugs have shown potential in both preventing and treating cancer, offering a novel approach to complement traditional cancer therapies.
Mechanisms of Action
Anti-inflammatory drugs exert their effects through various mechanisms, including:
- Inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine production: Anti-inflammatory drugs can block the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, which play a crucial role in promoting inflammation and cancer growth.
- Suppression of inflammatory signaling pathways: These drugs can interfere with inflammatory signaling pathways, such as the NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways, which regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory genes.
- Modulation of immune cell function: Anti-inflammatory drugs can modulate the function of immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells, reducing inflammation and enhancing anti-tumor immune responses.
Recent Results in Cancer Research
Clinical trials have demonstrated promising results for anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of various types of cancer, including:
- Colorectal cancer: Celecoxib, a COX-2 inhibitor, has been shown to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer recurrence and improve survival outcomes.
- Lung cancer: Aspirin, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID),has demonstrated efficacy in reducing lung cancer risk and improving survival.
- Breast cancer: Tamoxifen, an anti-estrogen drug with anti-inflammatory properties, has been effective in preventing and treating breast cancer.
- Prostate cancer: Curcumin, a natural compound with anti-inflammatory properties, has shown promise in suppressing prostate cancer growth and metastasis.
Potential Benefits of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Cancer Treatment
Incorporating anti-inflammatory drugs into cancer treatment regimens offers several potential benefits:
- Enhanced efficacy: Anti-inflammatory drugs can enhance the efficacy of traditional cancer therapies, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, by reducing inflammation-induced resistance.
- Reduced toxicity: Anti-inflammatory drugs may have fewer side effects compared to traditional cancer therapies, potentially improving tolerability and patient outcomes.
- Prevention: Certain anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs and aspirin, have shown potential in preventing cancer development.
- Improved outcomes: Clinical trials have demonstrated that anti-inflammatory drugs can improve survival outcomes, reduce tumor recurrence, and enhance overall patient quality of life.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the field of anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer research holds immense promise, there are still challenges to overcome and areas for future exploration:
- Patient selection: Identifying the patients who will benefit most from anti-inflammatory drugs is crucial to optimize treatment strategies.
- Combination therapies: Investigating the potential of combining anti-inflammatory drugs with other cancer therapies may enhance efficacy and overcome resistance.
- Long-term safety: Assessing the long-term safety and potential adverse effects of anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer treatment is essential.
- Novel drug development: Further research is needed to develop novel anti-inflammatory drugs with improved potency, selectivity, and efficacy against cancer.
The emerging role of anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer research is transforming the treatment landscape. By targeting inflammation, these drugs offer a novel approach to combat cancer, enhancing efficacy, reducing toxicity, and improving patient outcomes. Further research and clinical trials are warranted to fully understand the potential of anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer treatment and to optimize their use for the benefit of patients. As the field continues to evolve, the future holds great promise for the development of innovative anti-inflammatory therapies that will revolutionize cancer care.
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2943 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 320 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Russ Cheatham
Russ Cheatham John William Daniel Robinson
John William Daniel Robinson John Cacavas
John Cacavas Josh Caldwell
Josh Caldwell E P Ferguson
E P Ferguson Sean Madigan Hoen
Sean Madigan Hoen William Hubbell
William Hubbell Eduardo Galeano
Eduardo Galeano Pete Hamill
Pete Hamill Kay Brellend
Kay Brellend Jim Dell
Jim Dell John Mayer
John Mayer Gwendolyn Womack
Gwendolyn Womack Brian Alexander
Brian Alexander Liz Cademy
Liz Cademy David Young
David Young Hillary Hawkins
Hillary Hawkins Adrian Streather
Adrian Streather Jen Hatmaker
Jen Hatmaker Glenn Proctor
Glenn Proctor
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Clinton ReedUnlock Endless Style Possibilities with One Pattern, Interchangeable Pieces,...
Clinton ReedUnlock Endless Style Possibilities with One Pattern, Interchangeable Pieces,...
 Elias MitchellSeasons of Maine: A Literary Odyssey Through the Heart of a Coastal Paradise
Elias MitchellSeasons of Maine: A Literary Odyssey Through the Heart of a Coastal Paradise
 Isaias BlairHow To Collect Cash From Football Bets: The Ultimate Guide to Profiting from...
Isaias BlairHow To Collect Cash From Football Bets: The Ultimate Guide to Profiting from... Gilbert CoxFollow ·14.4k
Gilbert CoxFollow ·14.4k Mikhail BulgakovFollow ·18.6k
Mikhail BulgakovFollow ·18.6k Lord ByronFollow ·8k
Lord ByronFollow ·8k Duane KellyFollow ·19.6k
Duane KellyFollow ·19.6k Theodore MitchellFollow ·12.5k
Theodore MitchellFollow ·12.5k Felix CarterFollow ·2.1k
Felix CarterFollow ·2.1k Fletcher MitchellFollow ·2.5k
Fletcher MitchellFollow ·2.5k Aubrey BlairFollow ·5.2k
Aubrey BlairFollow ·5.2k

 Jamie Bell
Jamie BellUnlock Your Mind with "Ever Wonder Why And Other...
Prepare to...

 Robert Frost
Robert Frost30 Day Betting Challenge: Transform Your Betting Habits...
Are you tired of...

 Derrick Hughes
Derrick HughesWhat Is Victory In War? Unraveling the Enigma of Triumph
The Illusion...

 Jesse Bell
Jesse BellThe Shooters: A Gripping Presidential Agent Novel That...
Enter the Shadowy World of...

 Ernest Hemingway
Ernest HemingwayUnlocking the Theological Depths of Paul Claudel: An...
Prepare to embark on an...
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 2943 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 320 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |